About me
I defended my PhD at the National Institute for Applied Sciences, Lyon, France (INSA de Lyon) under the supervision of Hugues Berry. I am currently doing a postdoc at OIST in the Computational Neuroscience Unit headed by Erik De Schutter.
I work in the field of computational neuroscience and focus on modeling reaction-diffusion systems involving neuron-glia and glia-glia interactions. I am especially interested in how topological characteristics can influence dynamics in networks of cells (either neurons or astrocytes).
Research
Astrocytes: overlooked brain cells
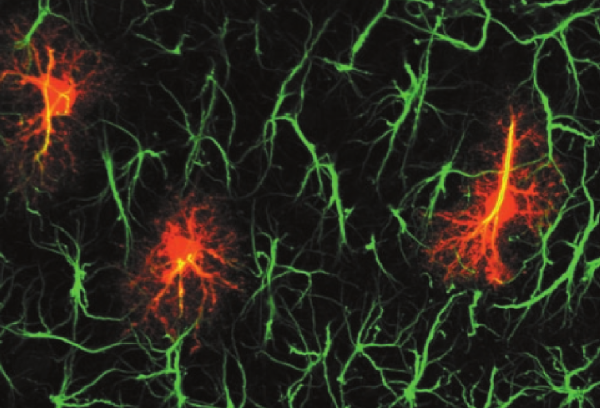
Figure 1: GFAP immunolabeling of LY-filled astrocytes (red) in CA1 stratum radiatum. Dye-filled astrocytes (red) show much more complex processes than what can be seen from GFAP immunolabeling (green). Taken from Bushong et al. (2002).
Over the last 20 years, astrocytes, a hitherto under-investigated type of brain cells, have gradually rose to prominence owing to multiple experimental discoveries. In contrast with neurons, these cells do not propagate electrical signals but communicate instead through changes in their intracellular calcium concentration. Recent discoveries indicate that, far from being isolated cells, astrocytes respond to neuronal activity and, although this is still controversial, seem to modulate synaptic transmission through the release of `gliotransmitter' molecules (in reference to neurotransmitters).
Like neurons, astrocyte are organized in networks (see Figure 1) and communicate their calcium activity by intercellular diffusion of second messengers, forming intercellular calcium waves. Two networks, one of neurons and the other of astrocytes, thus coexist in the brain; while neuronal networks have been the subject of intense experimental and theoretical investigations, astrocyte networks have been much less investigated. Notably, it was only discovered recently that astrocyte network topology could be more complex than what was previously thought.
Astrocyte network signaling
The mechanisms that drive calcium signaling in astrocytes are, at both subcellular and intercellular levels, still not completely understood. My research is thus mainly focused on the conditions needed to elicit astrocyte activity and on the specific role of network organization in inter-cellular calcium wave propagation.
Neuron to astrocyte communication
Neuron to astrocyte communication is usually adressed in the framework of the tripartite synapse: astrocytes sense neurotransmitter release at each synapses it enwraps and gets activated if neuronal stimulation is high enough (see Figure 2). Given that astrocytes organize into networks, they could differentially respond to neuronal stimulation depending on their coupling state.
Part of my work, together with Yael Hanein's experimentalist group at Tel-Aviv university, focuses on investigating astrocyte responses to neuronal stimulations by taking into account inter-astrocyte communication.
Inter-astrocyte communication
The mechanisms governing intercellular calcium wave propagation in astrocyte networks are not fully known either; notably, the effects of the recently documented network heterogeneity on calcium wave propagation have not been investigated. Once an astrocyte has been activated, e.g. by neuronal stimulation, it can propagate its activation to its neighbors, giving rise to intercellular calcium waves. The extent of these waves is however largely variable depending on the brain region investigated and / or the stimulation protocol used.
I'm interested in how the topology of astrocyte networks can control wave extent and network response to spontaneous activations. These questions can be investigated through the use of mathematical modeling and simulation. Movie 1 shows an example of simulated calcium wave propagation in a 3D modeled astrocyte network.
Publications
Book chapters
J. Lallouette, M. De Pittà, and H. Berry. Astrocyte networks and intercellular calcium propagation. In Computational Glioscience, pages 177--210. Springer, 2018. [ DOI | arXiv | http ]
Peer-reviewed publications
J. Lallouette, M. De Pittà, E. Ben-Jacob, and H. Berry. Sparse short-distance connections enhance calcium wave propagation in a 3d model of astrocyte networks. Frontiers in computational neuroscience, 8(45), 2014. [ DOI | http ]
G. Wallach*, J. Lallouette*, N. Herzog, M. De Pittà, E Ben Jacob, H. Berry, and Y. Hanein. Glutamate mediated astrocytic filtering of neuronal activity. PLoS computational biology, 10(12):e1003964, 2014. [ DOI | http ]
J. Lallouette and H. Berry. Topology drives calcium wave propagation in 3d astrocyte networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Complex Systems 2012, pages 453--463. Springer, 2013. [ DOI | http ]
Posters and Conference Abstracts
P. Biller, J. Lallouette, V. Liard, L. Guéguen, G. Beslon, and E Tannier. On the robustness of evolvability under different mutators. MCEB -- Mathematical and Computational Evolutionary Biology, 2018.
J. Lallouette, M. De Pittà, E. Ben-Jacob, and H. Berry. The topology of astrocyte networks controls the propagation of intercellular calcium waves. volume 15, page P205. 23rd Annual Meeting of the Organization for Computational Neurosciences, Québec City, Canada, July 26th-31st 2014. [ http ]
M. De Pittà, J. Lallouette, N. Liaudet, A. Volterra, E. Ben-Jacob, and H. Berry. Modelling of Ca2+ dynamics in astrocytic processes. 9th fens forum for neuroscience. 9th FENS Forum for Neuroscience, Milan, Italy, July 5th-9th 2014.
J. Lallouette and H. Berry. Topology drives calcium wave propagation in 3d astrocyte networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Complex Systems 2012, pages 453--463. Springer, 2013. [ DOI | http ]
J. Lallouette, M. Goldberg, M. De Pittà, E. Ben-Jacob, and H. Berry. The remarkable effect of network topology on calcium wave propagation in astrocyte networks. Multidisciplinary approaches to quantify astrocyte-neuron signaling, FENS Barcelona, Spain, 12th-14th July 2012 2011. [ .pdf ]
PhD thesis
J. Lallouette. Modeling calcium responses in astrocyte networks: Relationships between topology and dynamics. PhD thesis, INSA de Lyon, December 2014. [ .pdf ]
Teaching
Undergraduate department, INSA Lyon
Computer architecture
Codage_des_nombres.pdf - 580.8 kB
Correction_Codage.pdf - 127.3 kB
Algorithmics
Game_of_life.tar.gz - 2.4 kB
Object Oriented Programming with Java
Relational databases with SQL
correction_TD_AR.pdf - 102.3 kB
Correction_TD_RetroConception.pdf - 60.8 kB
Bioinformatics and Modelling department, INSA Lyon
Objected Oriented Programming with C++
Students needed to conceive and implement a C++ application simulating 2D collective boid-like movements. Individual elements needed to avoid obstacles and try to catch preys while avoiding predators.
projet3Bim2013.pdf - 312.4 kB
Project_3BIM_example.tar.gz - 12.8 kB
CV
CV.pdf - 85.3 kB
CV_french.pdf - 78.9 kB
